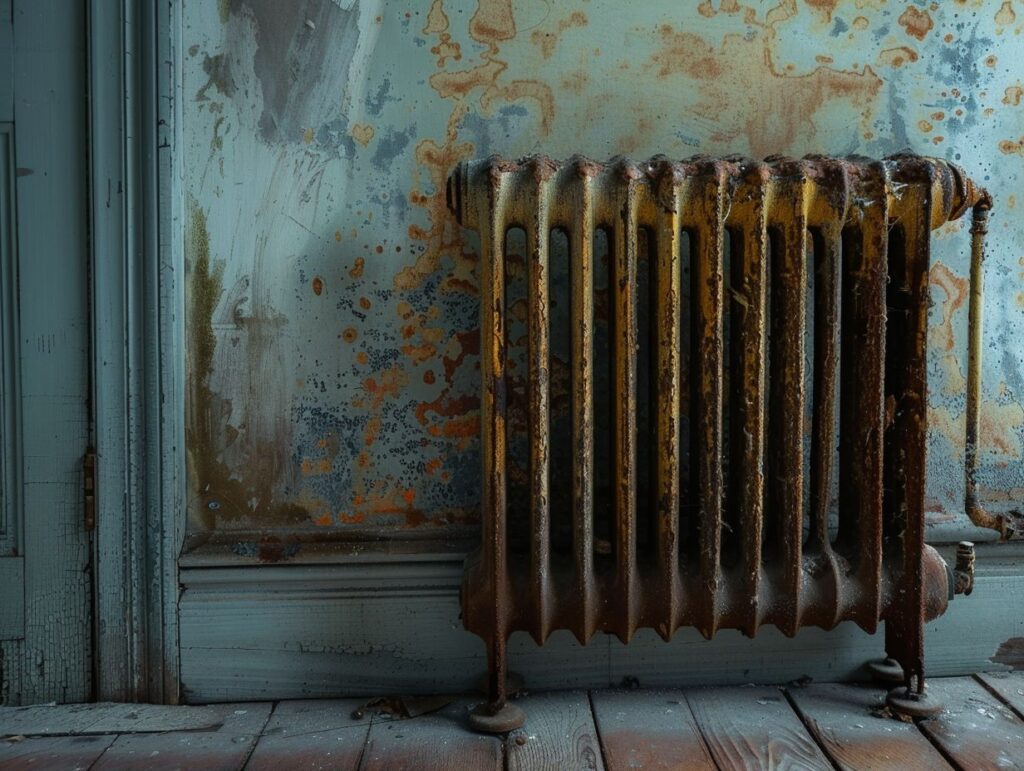
Radiators are essential components in many homes, offering warmth and comfort, especially in colder months. These fixtures are prone to rust as they age.
This article delves into the causes of rust formation on radiators, the indicators to watch for, and methods for preventing and addressing this prevalent issue. If you are contending with rusty radiators in your living space or elsewhere in your residence, expert tips and guidance are offered to assist you.
Key Takeaways:
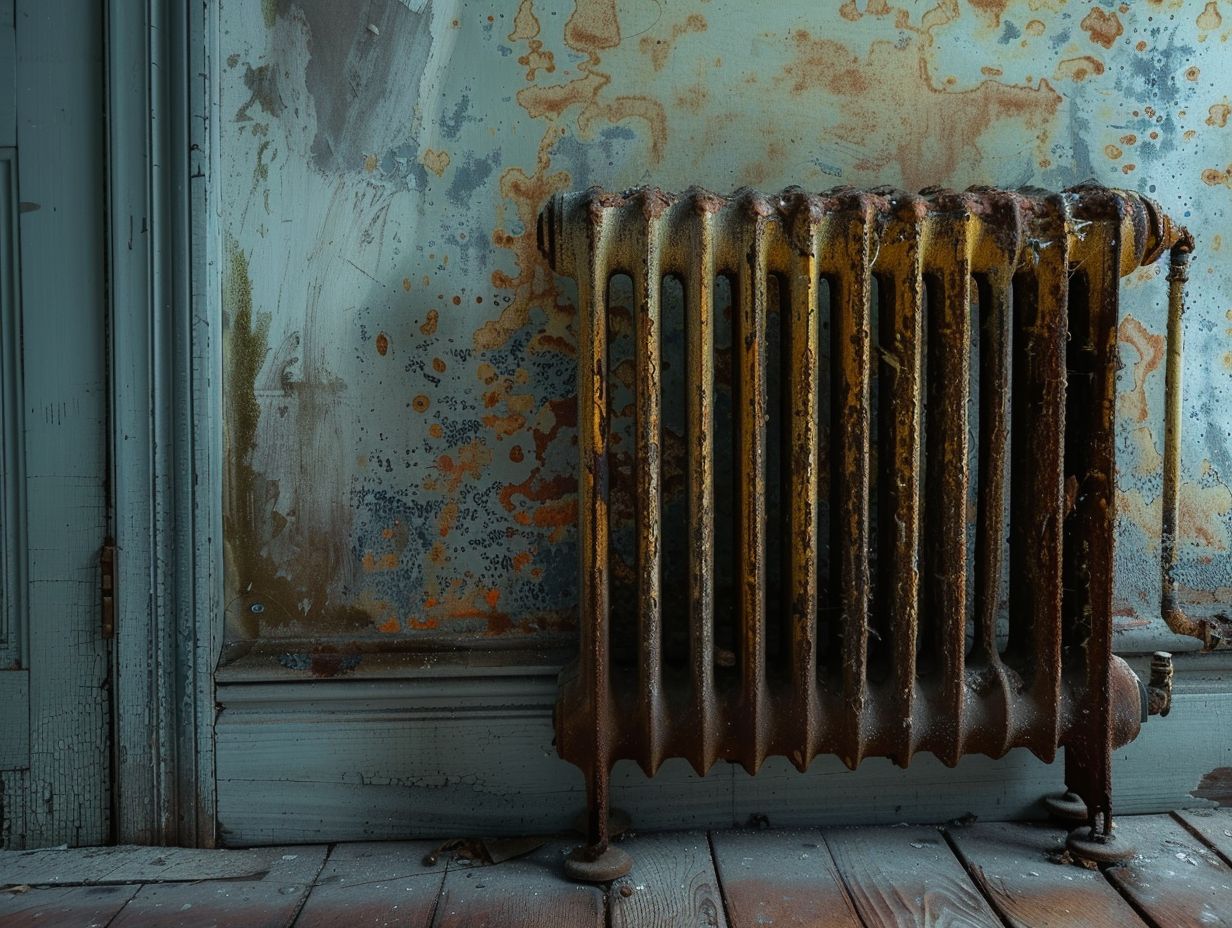
- Living room radiators can rust due to moisture, humidity, and age/wear.
- Signs of rust on radiators include visual indicators and performance issues.
- Maintenance and rust removal techniques can help prevent and treat rust on radiators, but replacement may be necessary in some cases.
Causes of Rust on Radiators
Rust on radiators can stem from various factors, including internal and external corrosion, the presence of sludge in the heating system, and prolonged exposure to moisture. A thorough understanding of these causes is essential for effectively preventing and addressing rust issues.
Internal corrosion occurs when the metal inside the radiator oxidises through chemical reactions with the water in the heating system. On the other hand, external corrosion results from exposure to elements such as oxygen and environmental pollutants.
The accumulation of sludge, typically a combination of debris and water, fosters an environment for rust-causing bacteria to thrive. The presence of water acts as a catalyst for the oxidation process, hastening the development of rust within the radiator.
These processes can have a significant impact on the radiator’s efficiency and lifespan, leading to decreased heating performance and potential system malfunctions if left unattended.
Moisture and Humidity
Moisture and humidity can accelerate the corrosion process on radiators, leading to the formation of rust. The presence of water in the heating system can create ideal conditions for corrosion to occur unless proper corrosion inhibitors are utilised.
When water comes into contact with the metal components of radiators, it initiates a chemical reaction that causes the metal to break down and form rust. This rust not only compromises the structural integrity of the radiator but also reduces its efficiency in heating up a space.
This is where corrosion inhibitors play a crucial role in protecting the radiator materials from this destructive process. By forming a protective barrier on the metal surface, corrosion inhibitors prevent water and oxygen from directly interacting with the metal, thus significantly reducing the chances of corrosion and prolonging the lifespan of the radiator.
Age and Wear
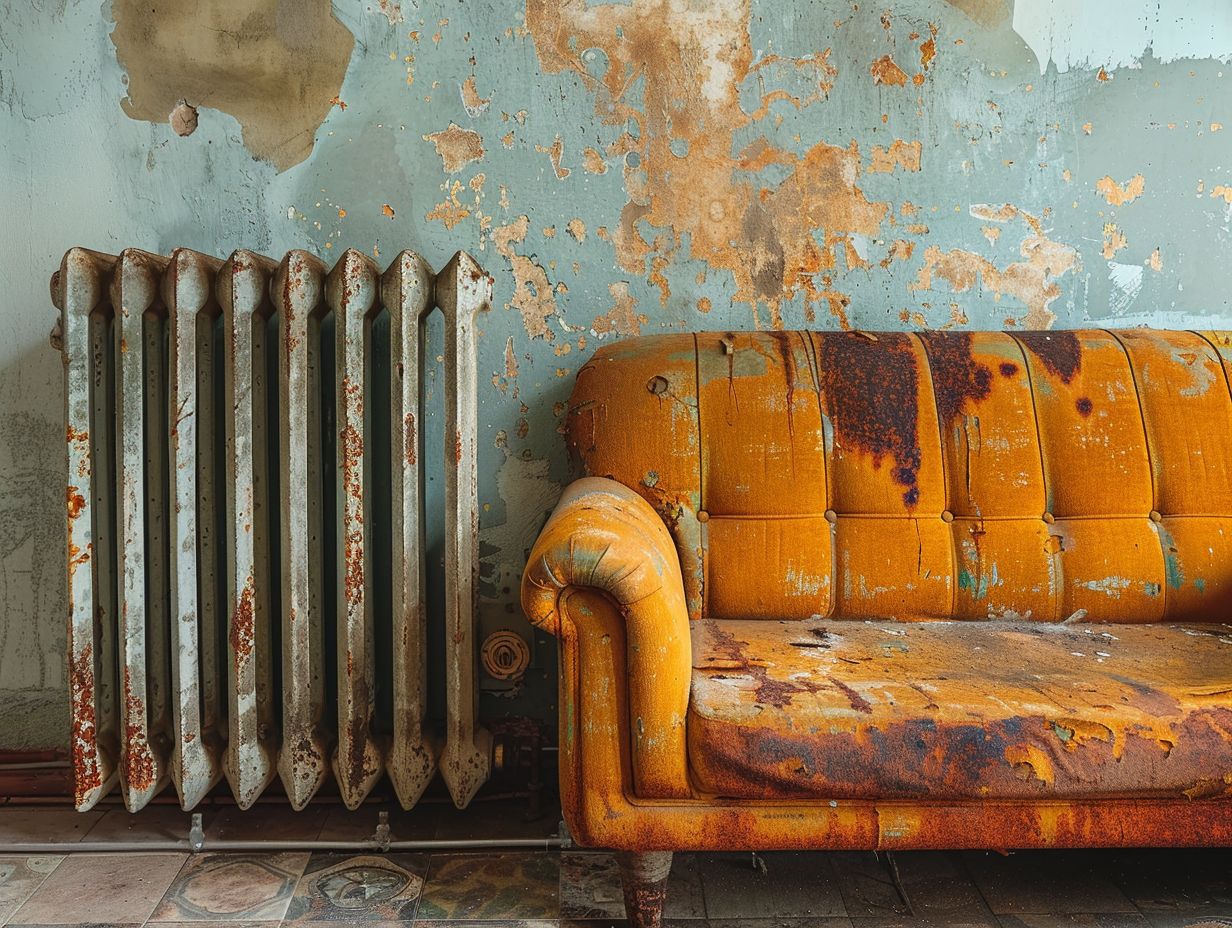

The age and wear of radiator components, especially those made of steel, can increase your susceptibility to rust and corrosion. Over time, the pipes and internal structures of your radiators may deteriorate, leading to potential leaks and reduced efficiency.
This deterioration in material integrity can not only compromise your heating system’s effectiveness but also pose safety hazards due to the weakened structure of the radiator.
The gradual build-up of rust within your system can restrict water flow, affecting the even distribution of heat in your space.
The rust particles can contaminate the water circulating through your radiator, potentially causing damage to valves and other components. Regular maintenance and inspections are vital to address these issues and prolong the lifespan of your radiators.
Signs of Rust on Radiators
Identifying signs of rust on radiators is crucial for timely intervention to prevent further corrosion and potential radiator leaks. Visual indicators and performance issues can serve as signals of rust-related problems that necessitate immediate attention.
Common visual signs of rust on radiators include discolouration, flaking paint, and visible corrosion spots. These indicators not only diminish the radiator’s aesthetic appeal but also point to underlying issues that could compromise the system’s performance.
For instance, inefficient heating, unusual noises, or inconsistent temperatures throughout the house may all stem from rust-related problems within the radiator. By addressing rust at its onset, you can circumvent expensive repairs and ensure the optimal functioning of the heating system.
Visual Indicators
Visual indicators of rust on radiators may manifest as discolouration, peeling paint, or rusty patches on the surface. These signs are particularly noticeable on radiators crafted from materials prone to corrosion.
For example, galvanic corrosion can expedite the rusting process when different metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte like water. Radiators made of steel or iron are more vulnerable to galvanic corrosion than aluminium or stainless steel radiators.
The material selection in radiators significantly influences their durability and ability to resist rust and corrosion.
Performance Issues
Performance issues associated with rust on your radiators can impact the efficiency and energy consumption of your central heating system. It is crucial to address corrosion early through preventive measures to uphold the optimal performance of your heating system.
Over time, the accumulation of rust within your radiators can result in decreased heat output. This can lead to certain areas of your home receiving insufficient heating while other areas become excessively warm. Such inconsistencies in heating can cause discomfort for occupants and create uneven temperature conditions throughout the space.
As corrosion advances, your heating system may need to work harder to compensate for these inefficiencies. This can result in increased energy consumption and higher utility bills.
By implementing preventive strategies like regular maintenance, utilising corrosion-resistant materials, and employing rust inhibitors, you can help mitigate these issues and ensure that your heating system operates efficiently.
Preventing and Treating Rust on Radiators
Preventing and treating rust on radiators in your heating system requires a multi-faceted approach that includes regular maintenance, thorough cleaning, and the application of appropriate chemical inhibitors to prevent corrosion. By taking proactive measures, you can prolong the lifespan of your radiators and the overall heating system.
For effective rust prevention on radiators, it is crucial to conduct regular maintenance. Scheduling annual inspections can help you detect early signs of corrosion and address them promptly.
Additionally, employing gentle cleaners and soft brushes during cleaning can remove dirt and grime without causing damage to the radiator surfaces.
The use of chemical inhibitors is essential in minimising corrosion by forming a protective barrier on the radiator surfaces. Monitoring the water quality and pH levels within the heating system is vital for controlling chemical reactions and preventing rust formation.
By regulating these reactions effectively, you can maintain the integrity of your radiators and ensure the optimal performance of your heating system.
Maintenance Tips
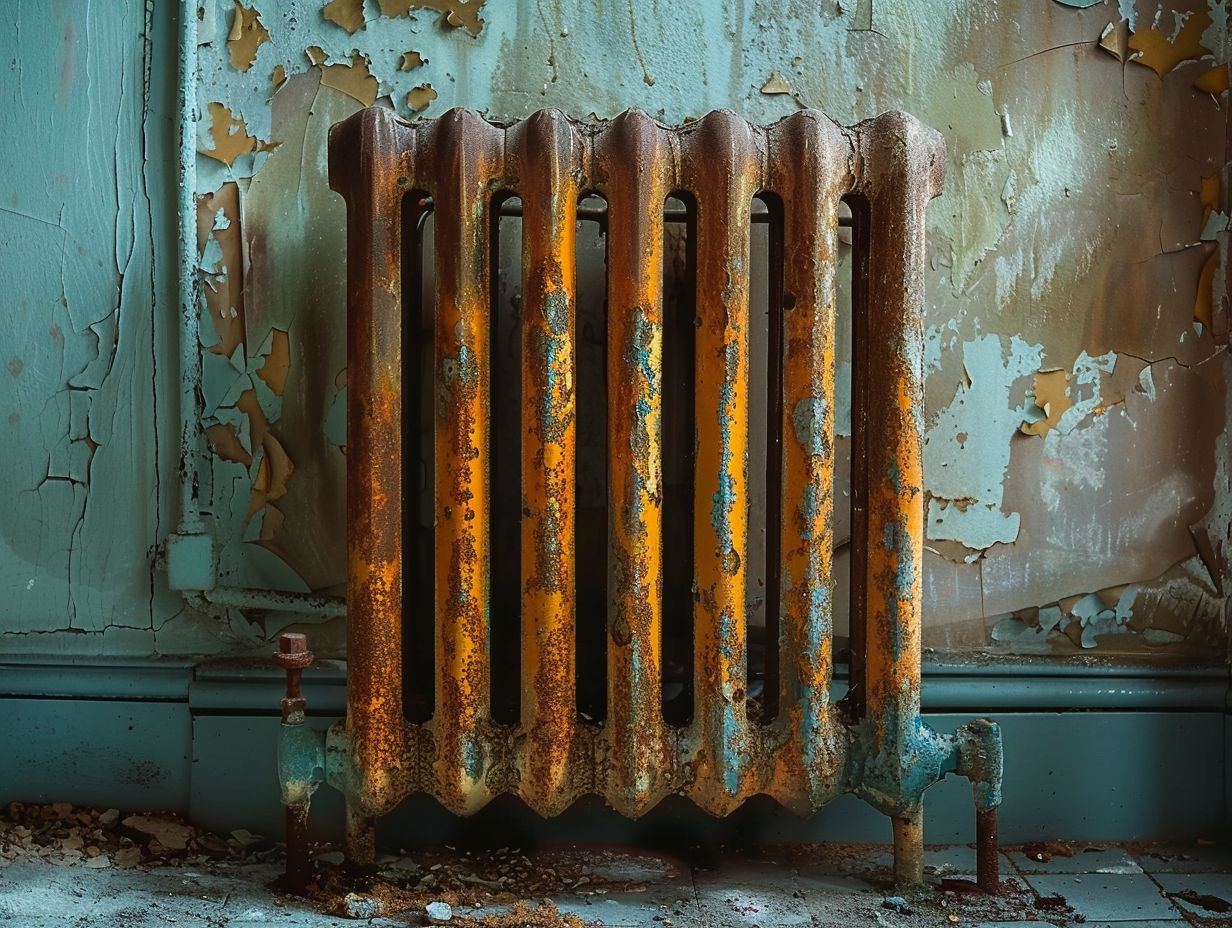

Regular maintenance of your radiators involves inspecting the boiler, checking valves for leaks, and ensuring proper circulation of water within your heating system. Maintaining these components is crucial for preventing rust and ensuring efficient heat distribution.
To keep your radiator functioning optimally, it is important to schedule regular boiler inspections to check for any signs of wear or malfunctions. Additionally, pay close attention to valve maintenance, tightening any loose connections and addressing leaks promptly to prevent water damage.
Regularly checking water circulation is essential to ensure that heat is evenly distributed throughout your system. By staying proactive with these maintenance tasks, you can extend the lifespan of your radiator and avoid costly repairs in the future.
Rust Removal Techniques
In terms of removing rust from radiators, the techniques you choose depend on the level of external corrosion and the presence of chloride compounds.
Utilising a combination of mechanical and chemical methods can effectively eliminate rust deposits and restore the radiator’s functionality.
Along with mechanical scraping and chemical treatments, an alternative method for addressing chloride-induced corrosion in radiators is the use of inhibitors. These inhibitors serve as protective shields, hindering rust formation and preventing further deterioration of the radiator.
It is essential to evaluate the type and severity of rust in the radiator to identify the most appropriate rust removal technique. Selecting the correct method can not only extend the radiator’s lifespan but also enhance its overall efficiency.
Replacing Rusty Radiators
When corrosion compromises the structural integrity of your radiator materials and affects the heating system’s performance, replacing rusty radiators becomes necessary. Selecting suitable replacement radiators is crucial for ensuring efficient heat distribution and preventing future corrosion issues.
Corrosion in radiators can be accelerated by factors such as exposure to moisture, chemicals in the water supply, or inadequate maintenance practices. Over time, this corrosion weakens the radiator’s metal, leading to leaks and inefficiencies in heat transfer.
To address these challenges, opting for durable materials like aluminium or stainless steel for replacement radiators becomes essential. These materials are more resistant to rust, thereby extending the lifespan of the heating system and minimising the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
When to Consider Replacement?
Understanding when to consider replacing rusty radiators is crucial for preventing further corrosion issues and optimising the efficiency of your heating system. By conducting regular maintenance and proactively monitoring your radiators, you can pinpoint the ideal time for replacement.
Recognizing indicators such as visible rust, leaks, inconsistent heating, or unusual sounds can serve as warning signs that your radiators require attention. Taking a proactive approach to addressing these signals enables homeowners to avoid expensive repairs and maintain continuous warmth throughout the colder seasons.
Incorporating preventive techniques like applying a corrosion-resistant coating or utilising a rust inhibitor can notably prolong the lifespan of radiators and enhance the overall effectiveness of the heating system.
Options for Replacement
When you are exploring options for radiator replacement, you need to consider factors such as central heating compatibility, maintenance requirements, and energy efficiency. Selecting the appropriate replacement radiators is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your heating system.
When you are choosing replacement radiators, it is essential to assess the size and heating capacity required for your space. For central heating systems, compatibility is key to ensure seamless integration.
The material of the radiators can impact their maintenance needs and longevity. Opting for energy-efficient models, like modern convector radiators or smart thermostatic radiators, can help lower heating costs and reduce energy consumption.
By evaluating your heating system’s needs and efficiency goals, you will be guided towards the most suitable replacement radiator options.
Frequently Asked Questions

What causes living room radiators to rust?
Living room radiators can rust due to a variety of factors, including moisture, condensation, and exposure to salt or other corrosive substances. Humidity levels, proximity to water sources, and the quality of the radiator’s coating can also play a role.
How can I prevent my living room radiator from rusting?
To prevent rust on your living room radiator, it is important to regularly clean and remove any dirt, dust, or debris that may be accumulating on its surface. Additionally, you can use a rust-inhibiting paint or coating to add an extra layer of protection against corrosion.
Do living room radiators made of different materials have different levels of susceptibility to rust?
Yes, living room radiators made of different materials can have varying levels of susceptibility to rust. Generally, aluminum and stainless steel radiators are less likely to rust compared to cast iron or steel radiators. However, the level of rust resistance also depends on the quality of the materials and their coatings.
How often should I check for rust on my living room radiator?
It is recommended to check for rust on your living room radiator at least once a year. However, if you live in a humid or coastal area, it may be necessary to check more frequently as these conditions can accelerate rust formation.
Can I repair rust on my living room radiator?
Yes, it is possible to repair rust on your living room radiator. If the rust is minor, you can sand it down and repaint the affected area. However, if the rust is extensive, it may be necessary to replace the radiator altogether.
Is rust on my living room radiator dangerous to my health?
In most cases, rust on your living room radiator is not harmful to your health. However, if the rust is accompanied by mold or mildew, it can potentially lead to respiratory issues. It is important to regularly maintain your radiator to prevent any potential health hazards.

